For US Healthcare Professionals
Mechanism of disease
Actor portrayal
Mechanism of disease
The role of hepatic lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in the excessive overproduction of oxalate in PH
The role of hepatic lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in the excessive overproduction of oxalate in PH
See what causes primary hyperoxaluria (PH) by watching the video below.
In the glyoxylate metabolic pathway, glyoxylate is normally recycled by a number of different enzymes in the hepatocyte.1,2
Normal glyoxylate metabolic pathway1,2

Touch image for larger view
In the 3 genetically defined subtypes of PH, a defect in 1 of 3 liver enzymes causes a deficiency in the glyoxylate metabolic pathway, resulting in the overproduction of glyoxylate.1-6
Dysregulated glyoxylate metabolic pathway1
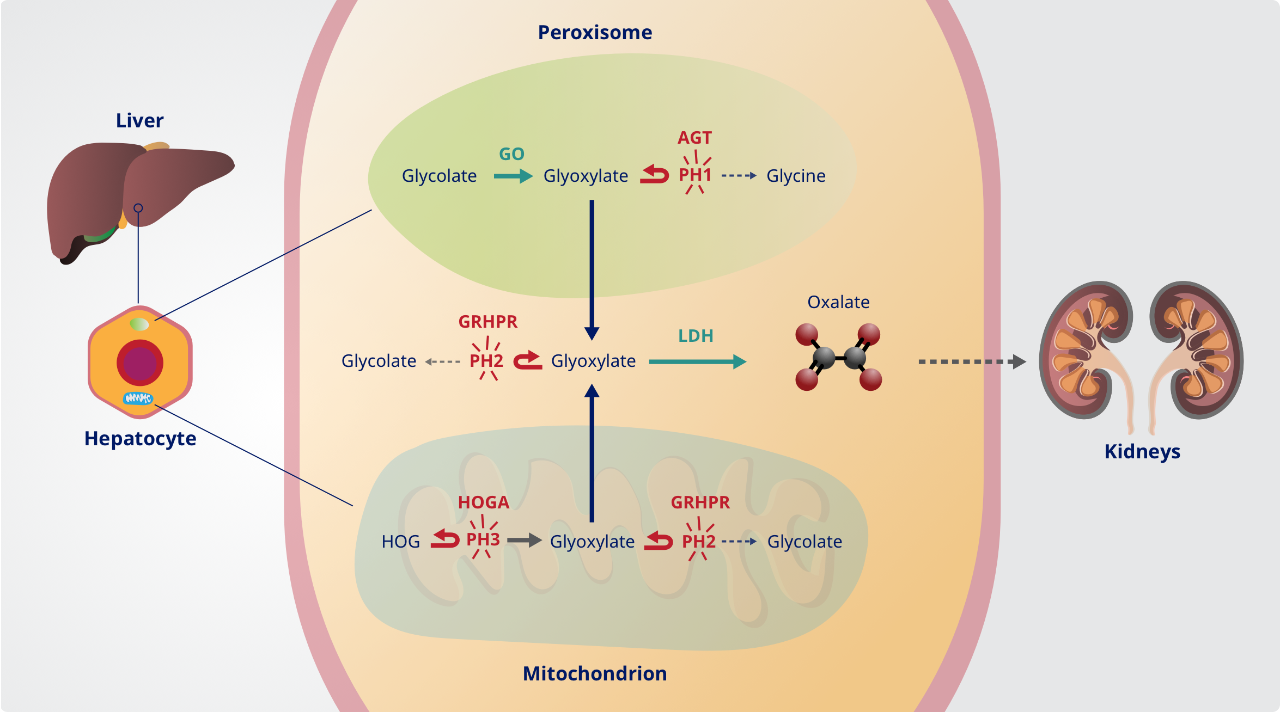
Touch image for larger view
In PH1, PH2, and PH3, hepatic LDH catalyzes the final common step in this pathway, converting abnormally high glyoxylate into excessive oxalate6
PH1
AGT enzyme deficiency
PH2
GRHPR enzyme deficiency
PH3
HOGA enzyme deficiency
Stay educated
Stay up to date with the latest news and information about primary hyperoxaluria.
References
- Martin-Higueras C et al. Molecular therapy of primary hyperoxaluria. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2017;40(4):481-489.
- Cochat P, Rumsby G. Primary hyperoxaluria. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(7):649-658.
- Belostotsky R et al. Primary hyperoxaluria type III—a model for studying perturbations in glyoxylate metabolism. J Mol Med (Berl). 2012;90(12):1497-1504.
- Riedel TJ et al. 4-hydroxy-2-oxoglutarate aldolase inactivity in primary hyperoxaluria type 3 and glyoxylate reductase inhibition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1822(10):1544-1552.
- Ben-Shalom E, Frishberg Y. Primary hyperoxalurias: diagnosis and treatment. Pediatr Nephrol. 2015;30(10):1781-1791.
- Lai C et al. Specific inhibition of hepatic lactate dehydrogenase reduces oxalate production in mouse models of primary hyperoxaluria. Mol Ther. 2018;26(8):1983-1995.

